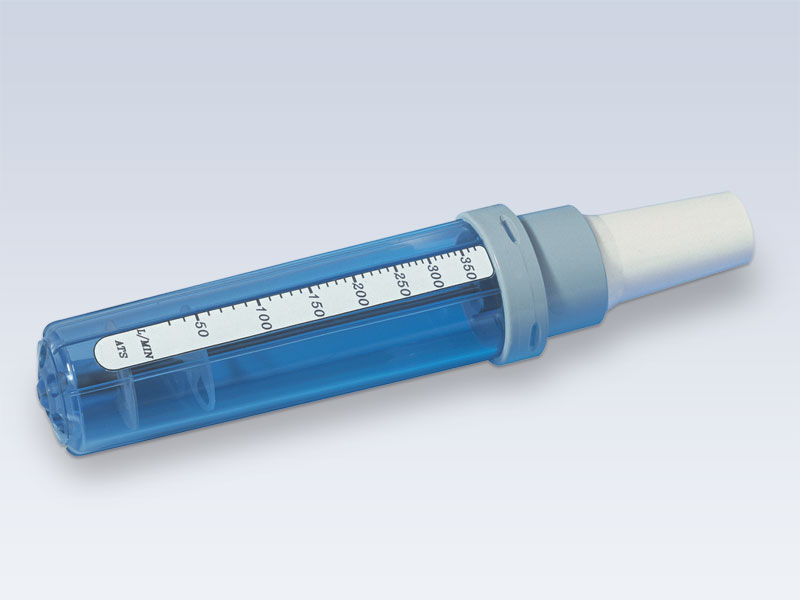
The In-Check is intended for patient use as a simple way to monitor inspiratory flow rates, providing valuable information about the degree of obstruction or restriction within air passages. It can also be used in the assessment of technique for inhaled medication.
- Measures nasal inspiratory flow for assessing nasal airway patency
- Train and enhance nasal breathing
- Assesses response to nasal provocation
- Allows home monitoring of Peak Nasal Inspiratory Flow (PNIF)
- Easy to use, clean and reset, the In-Check helps patients maintain their respiratory health
With the In-Check, you can accurately measure oral and/or nasal inspiratory flow rates (peak and sub-maximal) in order to assess suitability for inhaled medication.
Accuracy
- Each In-Check is individually calibrated to ensure a high degree of accuracy (+/- 10% or 10 L/min – whichever is greater)
- Inspiratory flow rates in the range of 30 L/min – 370 L/min can be measured
- US FDA 510k approved; conforms to international standards for peak flow meter performance
Features
- High-quality medical-grade stainless steel and plastic construction
- Sterilizable plastic mouthpiece accepts different mask sizes
- Simple enough for home patient use, rugged enough for routine clinic use
Ordering Information
Education/Clinicals
Product Description and Use
Application
- By breathing in through the In-Check, a cursor moves along the scale to indicate the inspiratory flow. The flow rate achieved can be noted by checking the position of the cursor against the calibrated scale.
- The In-Check may be used to measure either peak or sub-maximal inspiratory flows. The transparent body allows a qualitative view of the inspiratory manoeuvre.
- For the measurement of nasal inspiratory flows it is necessary to attach a facemask.
- For oral inspiratory flows, a clean mouthpiece (standard or filter type) should be used for each patient. The In-Check should be cleaned in accordance with instructions.
Product Warnings
How to Reset the In-Check
Resetting: To reset the In-Check, hold the instrument vertically with the mouthpiece uppermost so the rounded end of the meter can be tapped gently from underneath with your hand. The magnetic resetting weight will be dislodged and will return the cursor to a start position. When this has happened, invert the meter to return the magnetic weight to its resting position.
Instructions For Use
Oral Instructions
A low resistance Bacterial/Viral filter can be used to minimize the risk of cross-infection.
For oral peak inspiratory flows:
The patient should be asked to:
- Exhale fully
- Hold the In-Check horizontally with the lips sealed around the mouthpiece. A nose clip can be used to block the nostrils
- Inhale sharply and forcibly
- The inspiratory flow should be noted and the In-Check reset.
- The peak inspiratory flow should be measured three times and the highest result recorded.
For sub-maximal inspiratory flows (inhaler training):
The patient should be asked to:
- Exhale fully
- Hold the In-Check horizontally with the lips sealed around the mouthpiece.
- Inhale in a slow controlled fashion
- By advising the patient to inhale more or less forcibly, a described flow rate can be achieved.
Nasal Instructions
For peak nasal inspiratory flows:
The patient should be asked to:
- Exhale fully
- Hold the In-Check horizontally and ensure the face mask forms an airtight seal around the nose
- Inhale forcibly through the nose
- The inspiratory flow should be noted and the In-Check reset.
- The peak inspiratory flow should be measured three times and the highest result recorded.
- The peak nasal inspiratory maneuver should be a short, sharp inspiratory action of about one second in duration
- The inspiratory flow should be noted and the In-Check reset as above.
- The peak nasal inspiratory flow test should be repeated three times, and the highest result recorded in the patient’s records.
Note: Spectacles should be removed. The mouth must be closed.
- Care should be taken to ensure that the mask forms an airtight seal against the face. Different masks may be available in a variety of sizes to suit different facial shapes.
- The mask should be disinfected between patients to avoid the risk of cross-infection.
Peak Inspiratory Flow Measurement
Applications
Peak Inspiratory Flow Measurement
Peak Inspiratory Flow (PIF) is one of a multitude of spirometric measurements. PIF is generally measured on large spirometric machines and has not therefore been the subject of extensive serial home monitoring.
The In-Check product makes this prospect a reality and opens the door to a greater understanding of PIF.
Applications of Oral Inspiratory Flow Measurement
Measurements of sub-maximal inspiratory flows are valuable when training patients in the correct use of medical inhaler devices. Recent studies have indicated target inspiratory flows for many of the inhaled medication devices commonly used to deliver medication in respiratory diseases.
Feedback to the patient from In-Check measurement enables the patient to adjust their inhalation technique to best suit their own inhaler.
Applications of Peak Nasal Inspiratory Flow Measurement (PNIF)
Diagnosis of nasal obstruction
In some patients who complain of nasal obstruction, nasal airway patency is quite normal, and the symptom is due to consciousness of some other abnormality of the nasal cavity, such as a prominent turbinate. In other cases, surprisingly low readings are obtained in some patients, who are unaware of nasal obstruction, because they have got used to it. Quiet breathing through the nose can in such cases be achieved in spite of a peak nasal inspiratory flow reading as low as 50.
Such patients are often unaware that they breathe through the mouth for much of the time.
Reversibility of nasal obstruction can be assessed by measuring the PNIF after application of a nasal decongestant such as ephedrine by spray or drops. If the PNIF is not raised to a reading of over 100 by such treatment, then the obstruction may be associated with mucosa oedema, extensive polyps or anatomical abnormality. A trial of topical or systemic steroids may also bring the PNIF into the normal range (100 to 300 l/min).
Assessment of response to nasal provocation
Allergen or pharmacological mediator (e.g. histamine) application to the nasal mucosa in doses halving PNIF is usually associated with only minor and transient discomfort. Details of a simplified allergen provocation test have been published (ref. 1)
Home monitoring of PNIF
This may be useful in drug or immunotherapy trials in rhinitis, or for assessing the importance of environmental factors at home or work in individual patients with rhinitis. Cyclic changes in nasal airway patency can also be investigated, as can late responses to allergen provocation.
Normal Values and Performance Accuracy
PNIF
Repeated measurements on one occasion in trained subjects show a coefficient of variation of about 6%. Nasal airway patency varies with time and in many normal individuals the PNIF may vary in the course of a day by more than two-fold. Post decongestant readings are much more consistent, and consistency is also improved by avoiding factors associated with changes in the nasal airway, such as extremes of ambient temperature or humidity, spicy foods or irritant fumes etc.
Performance Accuracy
Accuracy +/- 10% or 10 l/min (whichever is greater) and repeatability of +/- 5 l/min.
Bibliography – Nasal PNIF
Cleaning
Instructions
- Immerse In-Check in warm (but not hot) mild detergent solution for 2-3 minutes (maximum 5 minutes. Agitate the meter to ensure proper cleaning.
- Rinse in warm water and shake to remove any excess water. It is important to rinse thoroughly to prevent salt spots appearing on the inside of the body and spindle.
- Allow to dry completely before using again.
The expected life of the In-Check, with normal use, is two years.
Ref. 1 M J Gleeson et al, Clin. Otolaryngol, 1986, 11, 99-107.
PO Box 6024
Granbury, TX 76049
1.800.848.8923 / 817.326.6357
Fax: 817.326.2182
© 2024 Alliance Tech Medical